|
|
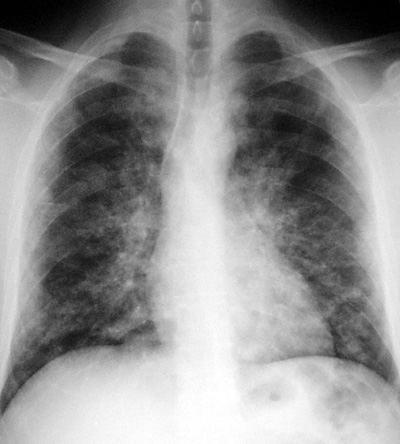
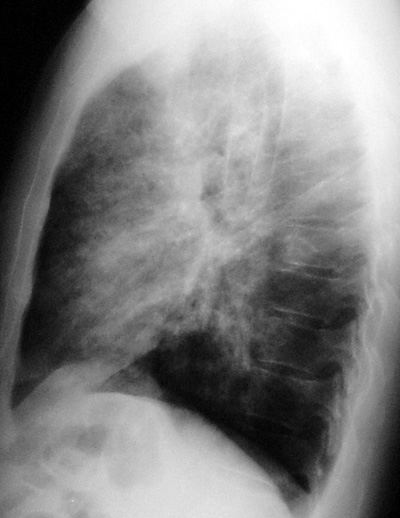
Alveolar Proteinosis
Alveolar Proteinosis is a disease of excessive surfactant production by type II pneumocytes. The alveolar spaces are slowly filled with surfactant.
CXR Findings: progressive perihilar airspace disease similar to pulmonary edema but with a normal heart size.
Clinical Clues: the disease slowly advances with progressive dyspnea and is treated by bronchoscopic lavage. These patients may have repeated chest infections, are prone to Nocardia infections and have an increased incidence of lymphoma.
"Aunt Sophies":
- Any diffuse bilateral airspace process: eg. pulmonary edema,
ARDS, bilateral hemorrhage eg. Goodpasture’s disease, lung contusion, aspiration, pneumonia.
- Diffuse tumors: eg. bronchoalveolar cell cancer, diffuse metastases with hemorrhage eg. renal cell carcinoma
- rarely: acute silicoproteiniosis
|