|
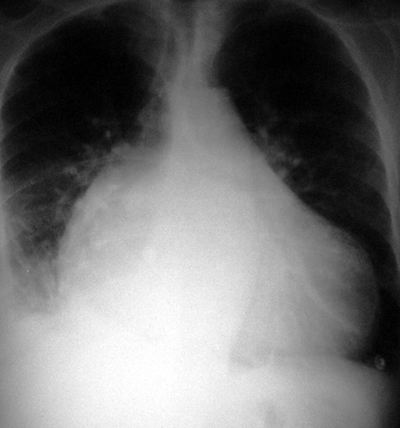 |
Cardiomyopathy
Pathophysiology: The cardiomyopathes can be classified as (1) congestive/ischemic (2) restrictive (3) hypertrophic. The commonest is congestive cardiomyopathy of ischemic etiology.
CXR Findings:
- enlarged, somewhat globular cardiac silhouette (>> 2:1) with multiple chamber dilation
- pulmonary congestion or pleonemia
- associated pulmonary edema
"Aunt Sophies":
- pericardial effusion
- rheumatic heart disease with multiple valve involvement
- rarely, pericardial cysts, pericardial tumors, various congenital heart disease (eg. Ebstein's anomaly in an adult)
A pericardial effusion is the commonest mimicker of congestive cardiomyopathy and the classic plain CXR "fat-stripe" sign is rarely seen. Echocardiography (or CT) is required to prove the presence of a pericardial effusion.
|