|
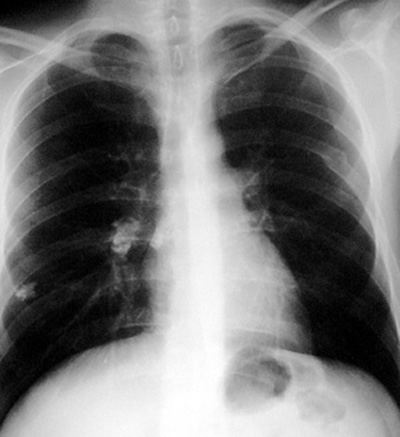
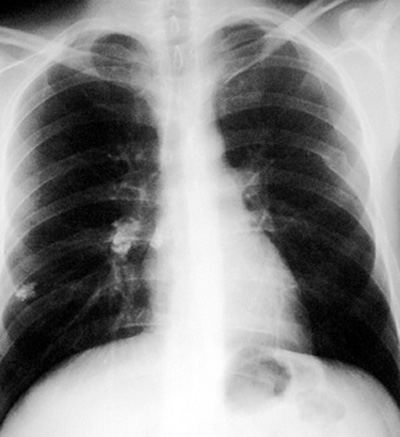
Ghon/Ranke Complex These are markers of tuberculous lung infection. They in themselves do not exclude active tuberculosis.
Pathophysiology: The initial non hyperimmune tuberculous pneumonia is in the lower 2/3 of the lungs, which are the most ventilated. The initial site of infection (eg. granuloma - may calcify) and the associated regional hilar adenopathy (may also calcify) form the Ghon/Ranke complex.
CXR Findings:
- peripheral lung nodule often with benign calcifications
- regional ipsilateral node(s) which may calcify
"Aunt Sophies":
- other granulomatous infection, especially fungal infections
- tumor with ipsilateral adenopathy
- other focal pneumonias with ipsilateral adenopathy (rare as these are rarely focal or nodular and generally do not calcify): eg. tularemia, anthrax, brucellosis, nocardia, Ebstein-Barr pneumonia
- treated lung cancer or lymphoma with dystrophic calcification
|