- This exam is done using the nasal route and a 12F Herlinger
duodenal tube with an end hole and a curved stiff wire. One can
use glide wires in different cases. A 8F Enteriflex Feeding
tube may also be used.
- Patients should receive instruction sheets explaining the
procedure and some of them may require sedation. With the 8F
Enteriflex tube, no sedation is required. Do not hesitate
to use Ativan sublingually or Valium IV since surgeons and
gastroenterologists should be aware that radiologists often use
sedation liberally.
- This exam is done using the nasal or the oral route.
- For intubations of the small bowel various small bowel
enteroclysis tubes have been used (see the TUBES subsection -
Equipment)
- 12F Herlinger or 14F Maglinte duodenal tube;
- With an end/side holes and a curved stiff wire.
- These tubes are useful in the presence of small bowel
obstruction for subsequent decompression
- Smaller gauge catheters
- Are being used more frequently
- 8F Enteriflex Feeding
- 8F Fredrick Miller tube feeding tube
- Easy, fast intubations
- Patients Preparation:
- Should receive instruction sheets explaining the procedure.
- Colon cleansing (two Dulcolax tabs night before)
- With the 8F catheters no sedation is required.
- Some may require sedation.
- Can use Ativan sublingually
- Rarely Diazemuls IV is given if patient has had uncomfortable
past experience.
Technique
- Spray the oropharnyx and nasal passages with Lidocaine spray
and use Xylocaine gel on a Q-Tip to anaesthetize the nasal
passage.
- Start an IV using a 22 gauge angiocatheter and give 10 mgm
Maxeran IV (to facilitate intubation) and/or Valium.
- Refer to “Clinical Radiology of Small Bowel” by Dr. D.
Maglinte and H. Herlinger regarding the technique and overcoming
problems of intubation.
Polibar (100% w/v) diluted to 80% w/v or 50% w/v is used
For normal small bowel use between 250-500 cc of barium. For
patients with an ileostomy or ileo-anal pouch use 120-180 cc of
barium.
Methylcellulose
About 1.5-2 litres of 0.5% of methylcellulose.
Important Points
- Barium is pumped at 110 cc/min and methylcellulose is infused
with a ‘dialysis’ pump at a rate between 75 and 140 cc/min.
- The tip of the Herlinger tube should always be in the proximal
jejunum.
- Should use Reglan (Maxeran) to speed up intubation into the
jejunum.
Radiographs
- All radiographs should be taken in both single and double
contrast phases. All single and double contrast films are done on
105 mm spot films. At least one 14 x 14 prone and supine
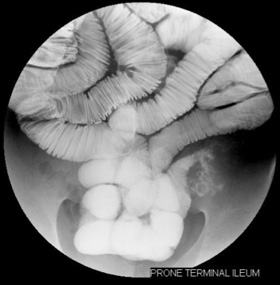
radiograph and spot 8 x 10 radiographs with compression of the
terminal ileum are done. Selected spot 10 x 12 radiographs of the
proximal, mid and distal small bowel in single and double contrast
are also taken.
- A Trendelenberg position with compression of the pelvic loops
can displace loops into the abdomen.
- Lateral view of pelvic loops is important to detect pelvic
mets/radiation strictures or entero-rectal fistulas.
- Tube angulation (cephalad or caudal) may “displace” pelvic
loops.
|
 |
| |
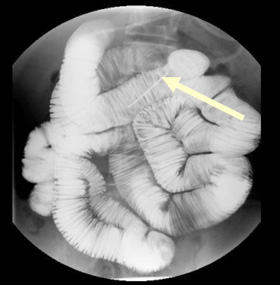
Note the arrow
pointing to the 8F Enteriflex tube. |
|
|