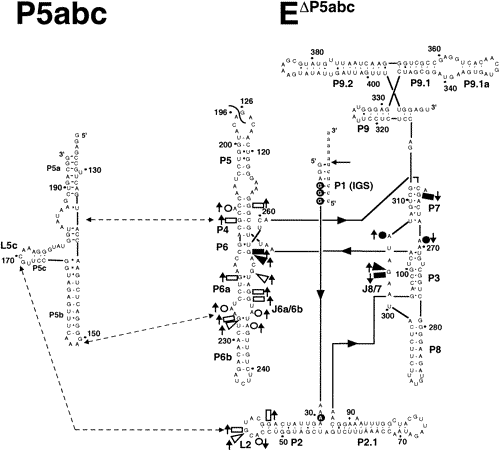

| Secondary structure of the T. thermophila L-21 ScaI EΔP5abc ribozyme and P5abc peripheral element. The oligonucleotide substrate is shown (lowercase letters) forming interactions with the IGS of the ribozyme, and the primary site of substrate oligonucleotide cleavage is marked by an arrow. Annotated residues have 2-fold changes in susceptibility to DMS or kethoxal modification in EP5abc compared to EP5abc·P5abc, with upward-pointing arrows indicating increased susceptibility to modification with P5abc removed and downward arrows the opposite. Of these positions, the open symbols represent residues that make direct interactions with P5abc in the crystal structure of the P4-P6 domain, or, in the case of L2, that are suggested by phylogenetic and mutational data to be making direct interactions. The closed symbols represent the residues not expected to make any direct interaction with P5abc. Wedges, rectangles, and circles denote changes detected by kethoxal, DMS (aniline cleavage), and DMS (reverse transcription), respectively. Positions with white text and underlying closed circles represent residues not expected to make direct interactions with P5abc that have modification patterns that are modulated by the binding of substrates. Positions 25-370 were assayed for changes in modification. from Engelhardt et al, Biochemistry 39:2639 |