|
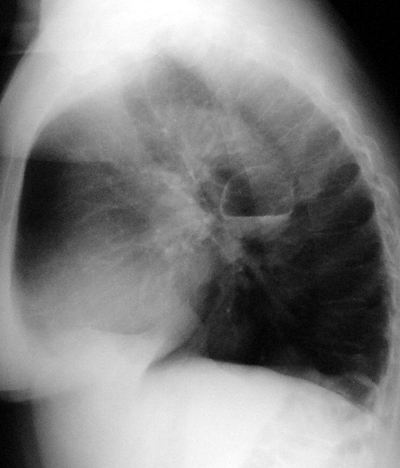 |
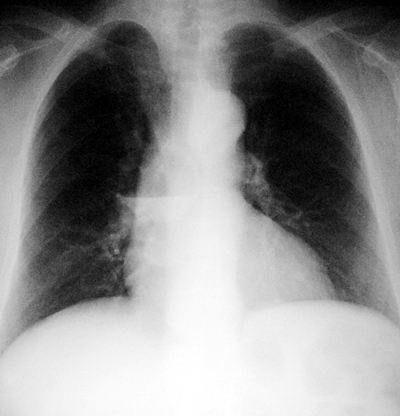
Bronchogenic Cyst
Pathophysiology: part of the spectrum of 'bronchopulmonary foregut' malformations that result from abnormal embryogenesis of the fetal foregut. The spectrum includes (1) bronchogenic cysts (2) esophageal duplication cysts (3) bronchial aplasia/dysplasia (4) pulmonary aplasia/dysplasia and (5) tracheo-bronchial fistulas
CXR Findings:
- very thin walled cyst usually several centimetres in diameter, most commonly seen in the middle or posterior mediastinum in the mid retro or infracarinal area
- second most common site is in the periphery of the lower lungs
Clinical/Radiological Clues:
Complications frequently occur, usually infection, with an air-pus fluid/blood level in the cyst. Infected bronchogenic cysts usually respond to antibiotic treatment, though rarely, a regional lung resection is done.
"Aunt Sophies":
- small bulla or bleb
- area of bullous emphysema
- pneumatocele
- old tuberculosis or fungal infection with thin walled cavities, or areas of air trapping
|