|
|
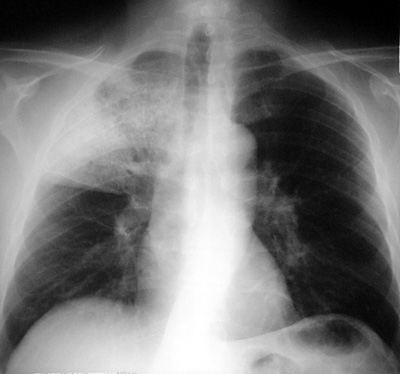
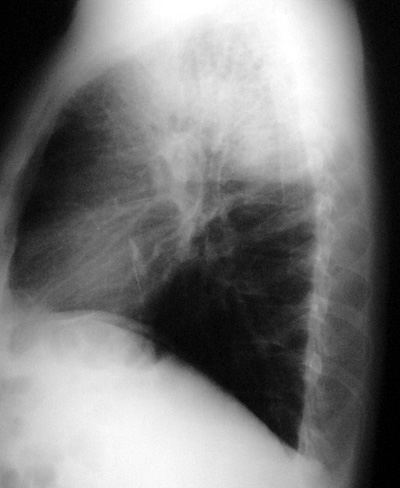
Lobar Pneumonia
Pathophysiology: Lobar pneumonia is the pneumonic consolidation of an entire lobe, lobes or lung itself. The term is of historic interest: today, the majority of pneumonia seen is segmental, or subsegmental in distribution. However, lobar pneumonia is still seen in the following patient subsets:
- Immuno-compromized or host suppressed patients
- Patients with poor health awareness or resources eg homeless, indigents, alcoholics
- Following chemotherapy and whole body radiation
- The elderly with underlying heart failure
CXR Findings: Non-specific: airspace disease with a lobar distribution, classic air bronchograms often seen, often associated with para-pneumonic pleural effusions.
Commonest Agent : Streptococcus pneumoniae
Clinical Clues: The larger the areas of pneumonia, bilaterality, and associated effusions are all bad prognostic signs.
"Aunt Sophies": Lobar atelectasis ± pleural effusions, lung hemorrhage, massive aspiration, unilateral pulmonary edema
|