
|
Main /
ProjectContextSensor technology has advanced to the point where it is possible to develop a distributed, autonomous, remote sensing and actuation system made up of tiny devices. The devices can now not only sense, but can also affect their surroundings or the objects to which they are attached, thus making them particularly suitable for use in automation applications. A collection of wirelessly networked tiny devices, with sensors and actuators attached, is often referred to as an embedded networked system (EmNet). EmNets are expected to substantially augment applications such as automotive, environmental monitoring, health care, enterprise management, and home/commercial automation.   The figures show the current generation of Berkeley Mote devices. In addition to being compact, the devices usually have 8-bit 8 Mhz microprocessors, 4 K RAM, built-in wireless radio and persistant storage in form of a flash memory. In addition, each device can host a number of sensors, and has a built-in 10-bit A/D converter.
 Mote-based RFID reader AutomationA typical automation application (e.g., factory floor automation) involves the management of equipment and resources in a manufacturing environment, as well as the control and monitoring of the manufacturing process. Automation applications can be difficult to create due to the number and variety of devices involved and complexity of the automation process itself. The organization and control of a number of devices, with a variety of sensors and actuators, in order to perform a task as a unit is difficult because it involves the distributed communication and coordination. Consequently, there is a need for middleware that simplifies the development of automation applications in distributed, through sensors driven environments. 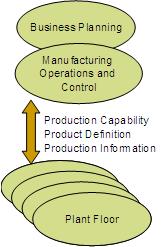 B2MML (Business 2 Manufacturing Markup Language) is an XML-based standard that aims to address the complexity of the automation application development, by allowing use of computer tools for definition and representation of manufacturing processes. B2MML describes manufacturing processes in terms of production capability, product definition and production information. Production capability describes manufacturing capabilities for a period of time; drives plans and schedules. Product Definition is basically a "recipe" of how a product is made. Production information conveys what to make, when to make it and production status (e.g. material usage, units of labor, equipment used). The figure shows B2MML as a bridge between business operations and manufacturing execution of business goals. MicroToPSS is a middleware system that allows automation applications to seamlessly integrate sensor/actuator networks into the manufacturing process by providing an environment for the execution of declaratively specified automation tasks (e.g., using B2MML for example).
MicroToPSS Application ModelMicroToPSS provides:
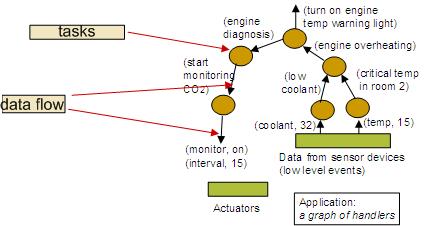 A number of tasks, specified in the scripting language, make up an automation application. A SQL-like language is used to configure data flows among tasks. Each sensor/actuator device can execute one or more automation tasks. The mapping of tasks to devices is done automatically. This mapping can be optimized at run-time in a way that is transparent to the application. |