|
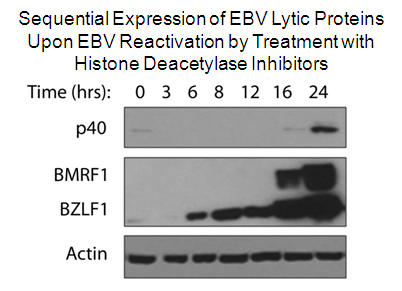
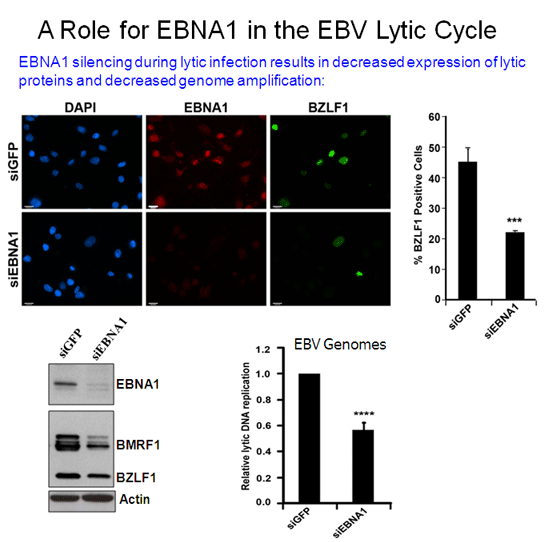
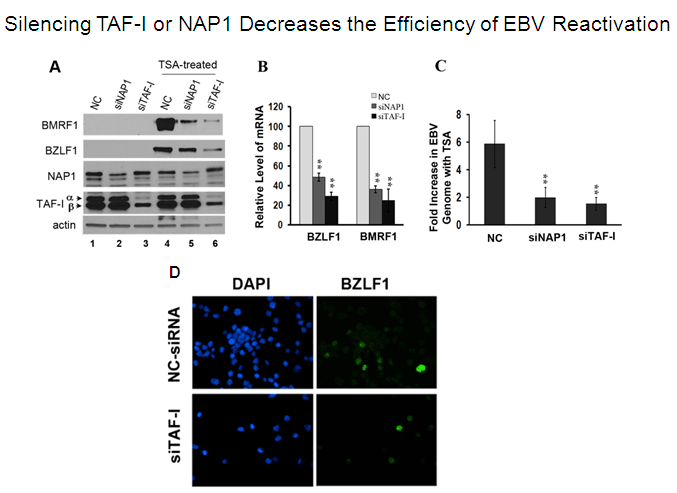
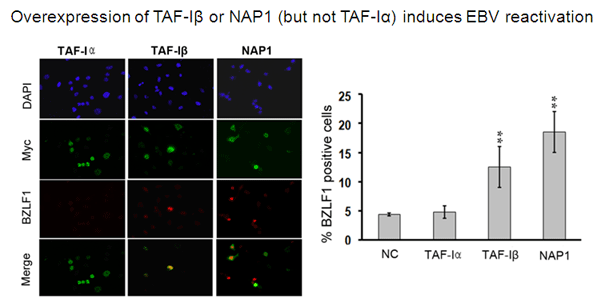
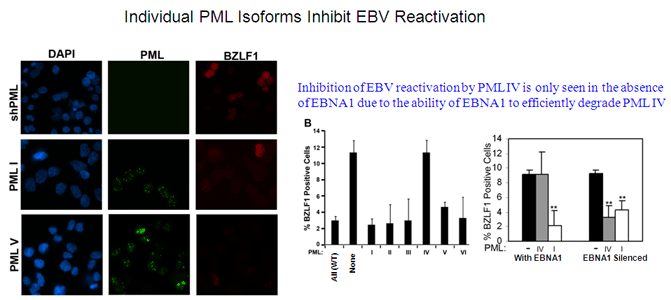
Infection of B-cells or epithelial cells by EBV usually results in a latent infection but, in both cell types, EBV can be reactivated to enter the lytic cycle. Reactivation starts with the expression of the viral BZLF1 protein, followed by BMRF1, then these two proteins act together to activate the ordered expression of the remaining lytic genes. During lytic infection, the viral genomes are amplified and packaged into virions for cell to cell and host to host spread. Since BZLF1 expression results in activation of the lytic cycle, how expression of this protein is controlled is key for understanding EBV reactivation. Reactivation of EBV to the lytic cycle is also a strategy used to kill EBV-positive tumour cells, since the lytically infected cells can be killed by ganciclovir treatment. Latent EBV genomes are complexed with nucleosomes and hence subject to the same epigenetic regulation as cellular DNA. In particular an increase in histone acetylation (eg. by treatment with deacetylase inhibitors) is known to turn on BZLF1. We have recently shown that two related histone chaperone proteins, NAP1 and TAF-I beta (also called SET), are important for activating BZLF1 expression and subsequent viral reactivation. We also found that, in addition to its multiple roles in latency, the EBV EBNA1 protein contributes to lytic infection, at least in part by overcoming the suppressive effects of PML nuclear bodies. Further studies are underway to better understand the epigenetic regulation of EBV reactivation and the contributions of EBNA1 to this process. |
|
| Publications:
Siddiqi, U.Z., Vaidya, A., Li, X., Marcon, E., Tsao, W.S., Greenblatt, J. and Frappier, L. 2019 Identification of ARKL1 as a Jun-interacting Factor that Negatively Regulates EBV Reactivation. In press.
Mansouri, S., Wang, S. and Frappier, L. 2013 A Role for the Nucleosome Assembly Proteins TAF-I beta and NAP1 in Activation of BZLF1 Expression and Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation. PLoS ONE 8(5):e63802. PMID:23691099
Malik-Soni, N and Frappier, L 2012 Proteomic Profiling of EBNA1-Host Interaction in Latent and Lytic Epstein-Barr Virus Infections. J. Virol. 86, 6999-7002. PMID: 22496234
Sivachandran, N. Wang, X.. and Frappier, L. 2012 Functions of the Epstein-Barr Virus latency protein, EBNA1, in viral reactivation and lytic infection. J.Virol. 86, 6146-58. PMID: 22491455
|
|