

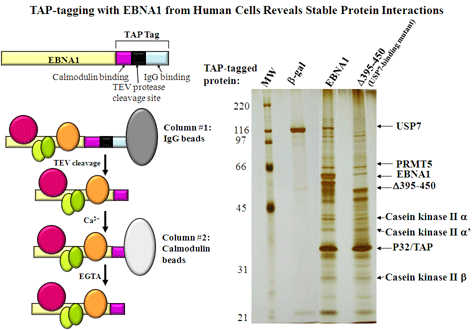
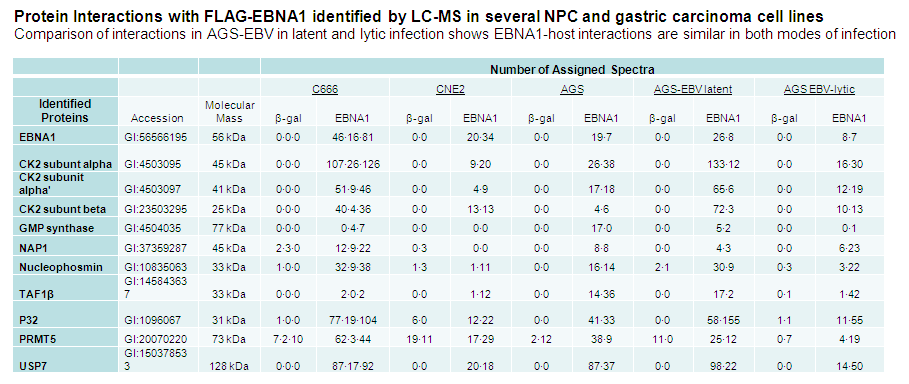
Malik-Soni, N and Frappier, L 2012 Proteomic Profiling of EBNA1-Host Interaction in Latent and Lytic Epstein-Barr Virus Infections. J. Virol. 86, 6999-7002. PMID: 22496234
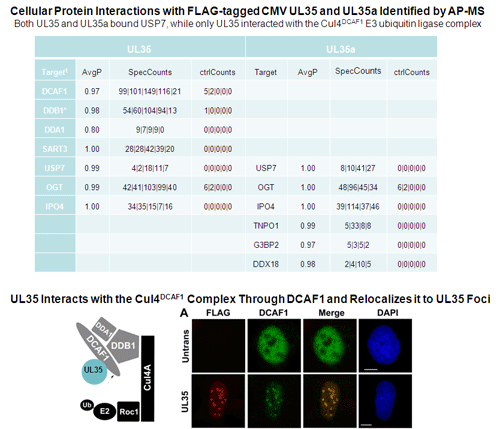
Salsman, J., Jagannathan, M., Paladino, P., Chan, P.-K., Dellaire, G., Raught, B. and Frappier, L. 2012 Proteomic Profiling of the Human Cytomegalovirus UL35 Gene Products Reveals a Role for UL35 in the DNA Repair Response. J. Virol. 86, 806-820. PMID: 22072767 (cover for vol 86 issue 4)
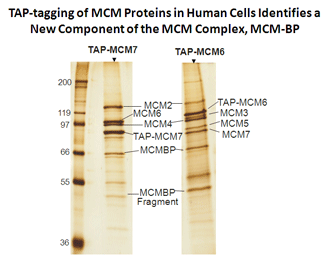
Sakwe, A.M., Nguyen, T., Athanasopoulos, V., Shire, K. and Frappier, L. 2007. Identification and characterization of a novel component of the human MCM complex. Mol Cell Biol. 27, 3044-3055. PMID:17296731
Hegde, N.R., Chevalier, M.S., Wisner, T.W., Denton, M.C., Shire, K. Frappier, L. and Johnson, D.C. 2006. The role of Bip in ER-associated degradation of major histocompatibility complex class I heavy chain induced by cytomegalovirus proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 20910-20919. PMID: 16731524
Saridakis, V., Sheng, Y., Sarkari, F., Holowaty, M.N., Shire, K., Nguyen, T., Zhang, R.G., Liao, J., Lee, W., Edwards, A.M., Arrowsmith, C.H. and Frappier, L. 2005 Structure of the p53-binding domain of HAUSP/USP7 bound to Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen 1: Implications for EBV-mediate immortalization. Mol. Cell 18, 25-36. PMID:15808506
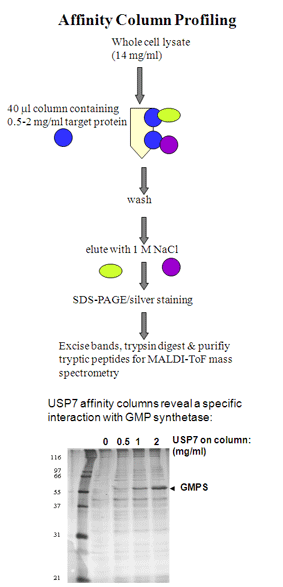
Holowaty, M.N., Zeghouf, M., Wu, H., Tellam, J., Athanasopoulos, V., Greenblatt, J. and Frappier, L. 2003. Protein profiling with Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 reveals an interaction with the herpesvirus associated ubiquitin specific protease, HAUSP/USP7. J.Biol. Chem. 278, 29987-29994. PMID: 12783858
Shire, K., Ceccarelli, D.F., Avolio-Hunter, T.M. and Frappier, L. 1999 EBP2, a human protein that interacts with sequences of the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 important for plasmid maintenance. J. Virol. 73, 2587-2595. PMID: 10074103