

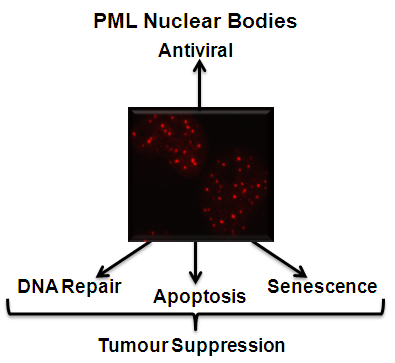
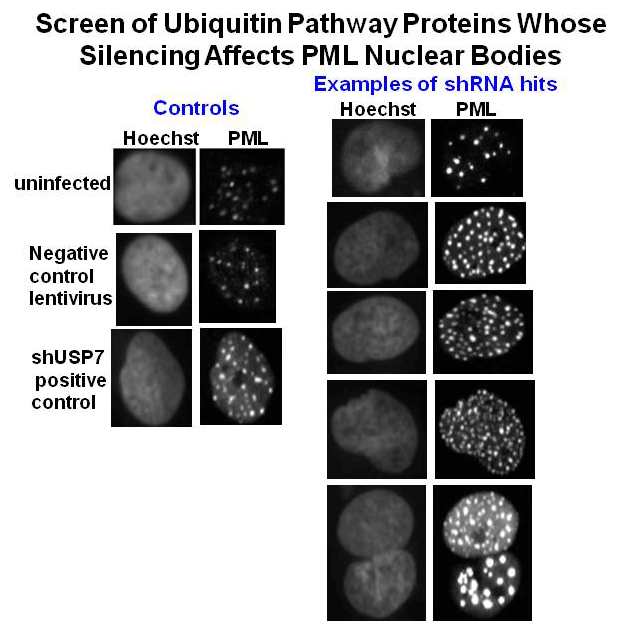
Despite their great importance as tumor suppressors, there is suprisingly little known about which cellular proteins regulate the turnover of PML proteins. We have recently conducted a screen of all cellular ubiquitin pathway proteins for their effects on PML nuclear bodies, leading to the identification of several potential regulators that are being further studied. In addition we have previously conducted a screen of over 200 herpesvirus proteins (from HSV-1, CMV and EBV) for those that disrupt PML nuclear bodies, resulting in the identification of several uncharacterized proteins that induce the loss or reorganization of PML bodies. Determining the mechanisms by which all of these proteins affect PML bodies will provide considerable insight into PML regulation.
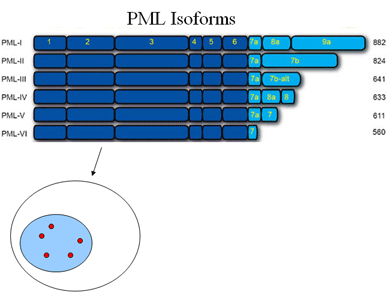
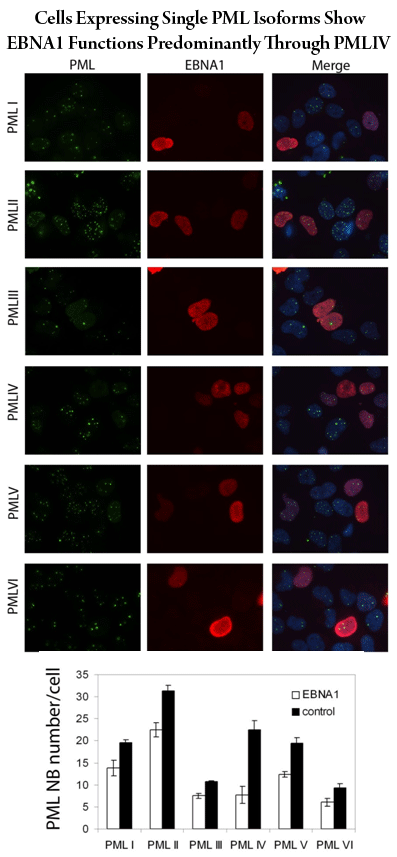
Finally, another interesting question is how the six different isoforms of PML contribute to the various functions and regulation of PML nuclear bodies. To study this question, we have built cell lines that express only one PML isoform (for each of PML I through VI) and have already used them to identify PML IV as the major isoform mediating regulation by EBNA1 and USP7. These cell lines will be valuable tools for dissecting the roles of the PML isoforms.
Publications:
Shire, K., Wong, A.I., Tatham, M.H., Anderson, O.F., Ripsman D., Gulstene, S., Moffat, J. Hay, R.T. and Frappier, L. 2016 Identification of RNF168 as a PML Nuclear Body Regulator. J. Cell Sci. 129(3):580-91
Cao, JY, Shire, K, Landry,C, Gish, G, Pawson, T and Frappier, L. 2014 Identification of a Novel Protein Interaction Motif in the Regulatory Subunit of Protein Kinase CK2 used by Viral and Cellular Proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol., 34, 246-258.
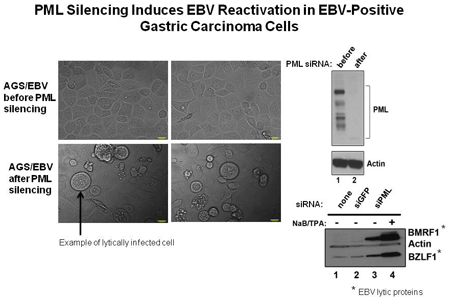
Sivachandran, N. Wang, X.. and Frappier, L. 2012 Functions of the Epstein-Barr Virus latency protein, EBNA1, in Viral reactivation and lytic infection. J.Virol. 86, 6146-58.
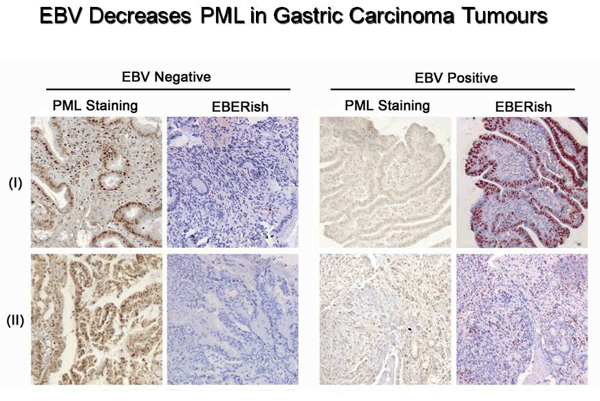
Sivachandran, N., Dawson, C.W., Young, L.S., Liu, F., Middeldorp, J. and Frappier, L. 2012 Contributions of the Epstein-Barr Virus EBNA1 Protein to Gastric Carcinoma. J. Virol. 86, 60-68.
Salsman, J., Wang, X. and Frappier, L. 2011 Nuclear Body Formation and PML Body Remodeling by the Human Cytomegalovirus Protein UL35. Virology, 414, 119-129.
Sarkari, F, Wang, X., Nguyen, T and Frappier, L. 2011 The Herpesvirus Associated Ubiquitin Specific Protease, USP7, as a Negative Regulator of the PML Proteins and PML Nuclear Bodies. PLoS One, 6(1): e16598. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016598
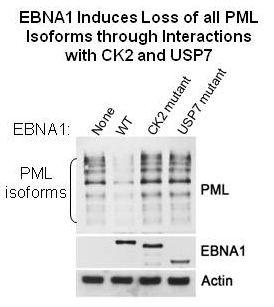
Sivachandran, N., Cao, J.Y. and Frappier, L. 2010 Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen 1 Hijacks the Host Kinase CK2 to Disrupt PML Nuclear Bodies. J. Virol. 84(21) 11113-11123.
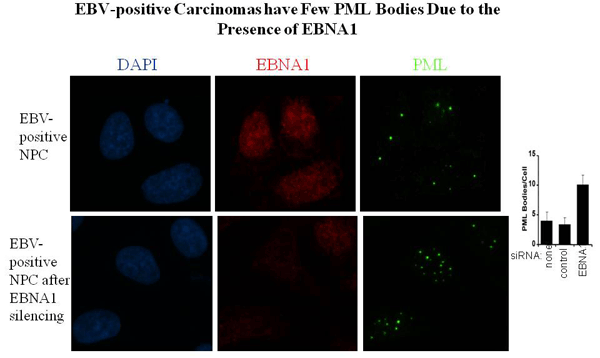
Sivachandran, N., Sarkari, F. and Frappier, L. 2008 Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen 1 Contributes to Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through disruption of PML Nuclear Bodies. PLoS Pathogens, 4(10): e1000170. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000170.
Salsman, J., Zimmerman, N., Chen, T., Domagala, M. and Frappier, L. 2008 Genome-wide Screening of Herpes Simplex virus, Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus Proteins for Subcellular Localization and Alteration of PML Nuclear Bodies. PLoS Pathogens 4(7): e1000100. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000100