

Salamun, S.G., Sitz, J., De La Cruz-Herrera, C.F., Marcon, E., Greenblatt, J., Fradet-Turcotte, A. and Frappier, L. 2019 The Epstein-Barr Virus BMRF1 Protein Activates Transcription and Inhibits the DNA Damage Response by Binding NuRD. J. Virol. In press.
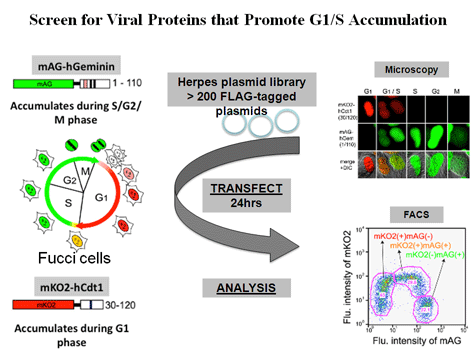
Paladino, P., Marcon, E., Greenblatt, J. and Frappier, L. 2014 Identification of Herpesvirus Proteins that Contribute to G1/S Arrest. J. Virol. 88, 4480-4492.
Salsman, J., Jagannathan, M., Paladino, P., Chan, P.-K., Dellaire, G., Raught, B. and Frappier, L. 2012 Proteomic Profiling of the Human Cytomegalovirus UL35 Gene Products Reveals a Role for UL35 in the DNA Repair Response. J. Virol. 86, 806-820. PMID: 22072767 (cover for vol 86 issue 4)
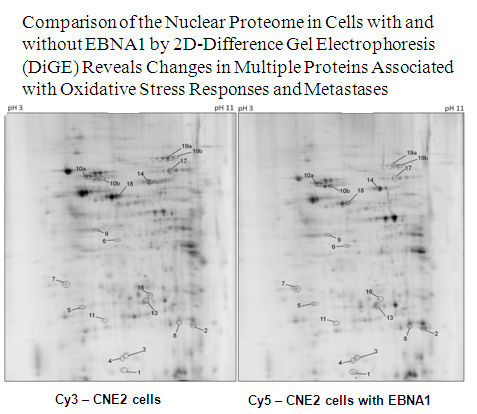
Cao, J. Y., Mansouri, S. and Frappier, L. 2012 Changes in the nasopharyngeal carcinoma nuclear proteome induced by the EBNA1 protein of Epstein-Barr virus reveal potential roles for EBNA1 in metastasis and oxidative stress responses. J. Virol. 86, 382-394. PMID: 22013061
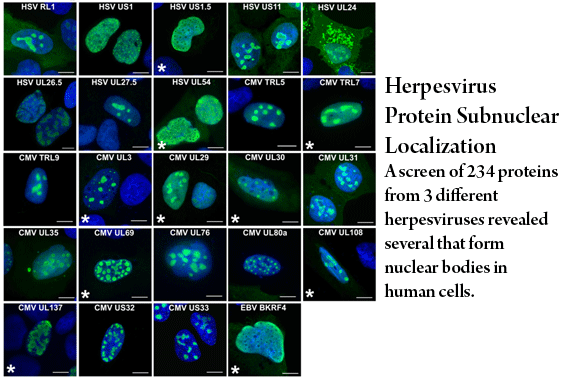
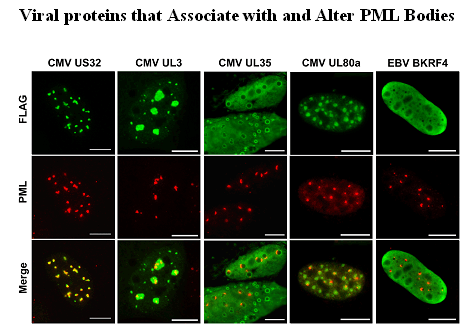
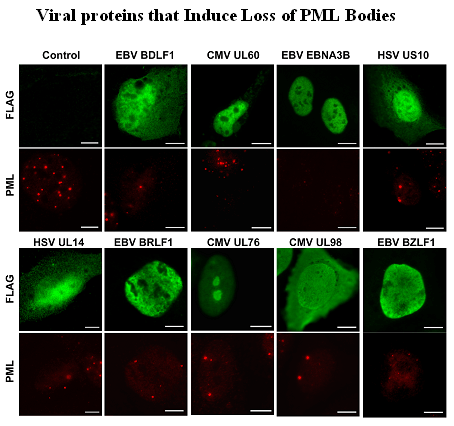
Salsman, J., Zimmerman, N., Chen, T., Domagala, M. and Frappier, L. 2008 Genome-wide Screening of Herpes Simplex virus, Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus Proteins for Subcellular Localization and Alteration of PML Nuclear Bodies. PLoS Pathogens 4(7): e1000100. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000100
Maxwell, K.L. and Frappier, L 2007 Viral Proteomics. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 71(2), 398-411.
Gao, M., Brufatto, N., Chen, T., Murley, L.L., Thalakada, R., Domagala, M., Beattie, B., Mamelak, D., Athanasopoulos, V., Johnson, D., McFadden, G., Burks, C. and Frappier, L. 2005 Expression Profiling of Herpesvirus and Vaccinia Virus Proteins using a High-Throughput Baculovirus Screening System. J. Proteome Research 4, 2225-2235. PMID: 16335970
Holowaty, M.N., Zeghouf, M., Wu, H., Tellam, J., Athanasopoulos, V., Greenblatt, J. and Frappier, L. 2003. Protein profiling with Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 reveals an interaction with the herpesvirus associated ubiquitin specific protease, HAUSP/USP7. J.Biol. Chem. 278, 29987-29994. PMID: 12783858