 |
Samuel Richard Ph.D. student Medical Biophysics University of Toronto |
||
|
Research
Academic
Pretty fun
stuff
Coffee break stuff
|
Flat-panel detectors
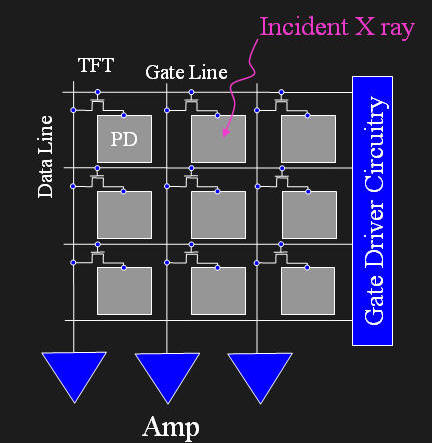
Basically, flat-panel detectors (FPDs) are to film radiography what digital cameras are to film cameras. They allow the readout of a digital images in the order of 1 sec or less with the use of a thin-film transistor (TFT) matrix as shown below in a simplified 3x3 array (typical detector have >1000x1000 arrays of pixels).
In an indirect detector, incident x-rays are converted to photons which
are then converted into an electric signal with a photodiode (PD). The
signal is then amplified and read out
line by line across the data line by sequentially turning on the gate line
for each column.
Flat-panel detectors are ideally designed for high-performance dual-energy imaging because they have fast readout capabilities, excellent signal-to-noise ratio and are inherently digital. The signal and noise performance of FPDs can be modeled analytically with the use of cascaded systems analysis.
|
||