|
Research
Dual-energy x-ray imaging
Flat-panel detectors
Cascaded systems analysis
Model observers
Publications
Academic
U of T Home
MBP Home
Pretty fun
stuff
Bicycling
Photography
Coffee break stuff
NYC Bike Snob
Apple Movie Trailers
Contact Info
|
|
Model Observers
The Hotelling model observer
Is an image really worth a 1000 words? Mathematically derived model
observers can be used to sum up the essential information into a single
number, the detectability index denoted: d'.
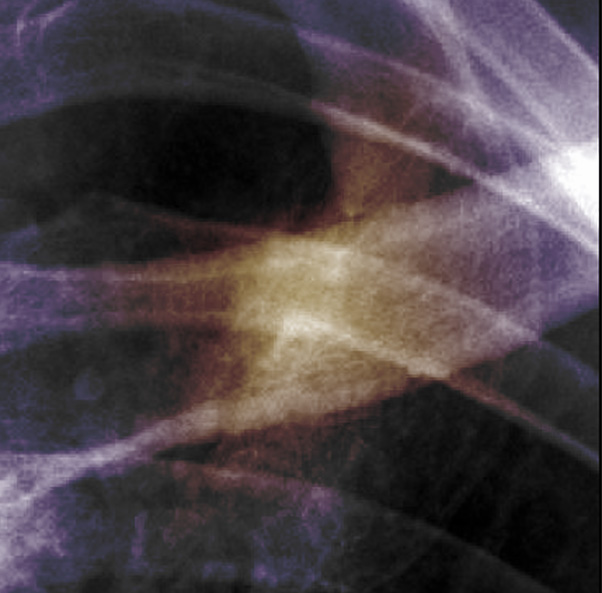
Consider the following four images as an illustrative example:
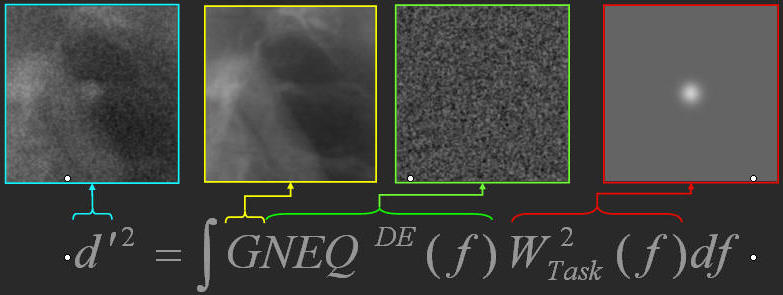
The
NEQ(f) describes the quantum noise
present in an image, in this case, the quantum noise in a
dual-energy x-ray image. The noise
equivalent quanta (NEQ) for FPDs can
measured experimentally or determined theoretically using
cascaded systems analysis.
The "G"
in the GNEQ(f)
corresponds to the "Generalization" of the noise which also
includes anatomical "clutter" or noise. Generally
anatomical noise is determiner empirically.
Wtask(f)
describes the given imaging task. It is described mathematically as the
Fourier difference of the "object absent" and "object present" signal. In this case the task
describes the detection
of a Gaussian sphere.
Finally, The
d'
called the detectability index predicts theoretically how well a
human observer is expected to perform the given task.
The detectability index can be compared with a threshold in order to
determine if "yes" or "no" the task would generally be successful.
References:
|