Diagnosis - RNA based Prion Disease Diagnostic Tools
Section Navigator> Diagnosis>
> Endogenous RNA extract & PMAC
> mRNA markers
> RNA aptamers
Endogenous RNA extract & PMAC
The protein misfolding cyclic amplification (PMCA) can amplify PrpRes from a mixture of normal hamster brain homogenate and 1:50 dilution of PrpSC (1). PMCA with the addition of endogenous, single stranded RNA extract from hamster brain homogenates stimulated PrpRes amplification by 10 fold compared PMAC in the absence of RNA addition (2). This finding provides evidence that RNA may be one of the conversion factors. Addition of single strand RNA extracts in combination with PMCA method is a more sensitive diagnostic tool in the early detection of low quantities of PrpSC from Prion diseased-infected individuals (2). This method may also be applied to detect Prion diseases even before the observable changes (such as spongiform formation) occur(3).
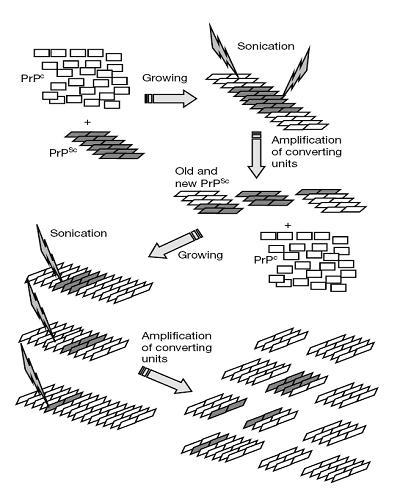
Figure 1: The modified schematic diagram for the PMAC method without the addition of RNA extract. (Adapted from Saborio GP et al. (3)) The amplification is based on incubation of of PrpSC with excess PrpC followed by sonication. Sonication disrupts the PrpC-PrpSC aggregate, producing more reaction sites for the next cycle of PrpRes formation. The total amount of Prp Res was detected via Western blot.
References:
(1) Supattapone S. Prion protein conversion in vitro. J. Mol. Biol. 2004; 82: 348-356.
(2) Deleault NR, Lucassen RW, Supattapone S. RNA molecules stimulate Prion protein conversion. Nature 2003;425:727-720.
(3) Saborio GP, Permanne B, Soto C. Sensitive detection of pathological Prion protein by cyclic amplification of protein misfolding. Nature 2001; 411:810-813.

